Compilation Pipeline
The code transformation for defined flavors involves several steps. This chapter describes the processing phases and configuration options.
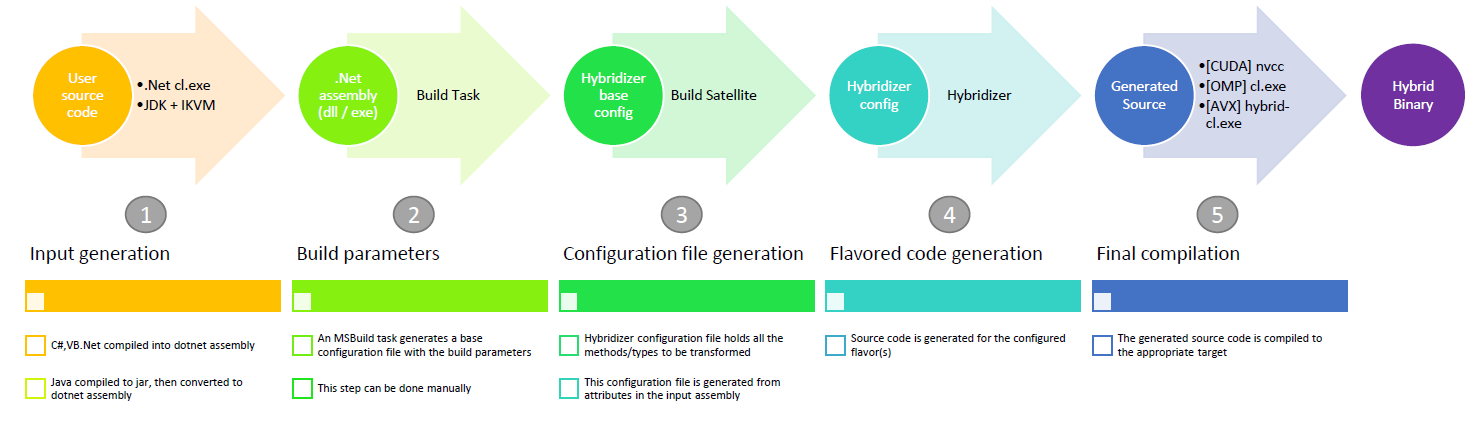
Pipeline Overview
Step 1: Input Generation
The user compiles code using standard tools:
| Source Language | Compiler | Output |
|---|---|---|
| C# | csc / Roslyn | .NET assembly (.dll) |
| F# | fsc | .NET assembly |
Step 2: Build Parameters
Several parameters control how source code for a given flavor is generated. The base configuration file (hybridizer.base.config) is generated using an MSBuild build task.
MSBuild Task Example
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<Project DefaultTargets="Build" xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/developer/msbuild/2003" ToolsVersion="4.0">
<PropertyGroup>
<HybridizerBuildTask>{HybridizerPath}\Hybridizer.VSIntegration.BuildSatelliteTask.dll</HybridizerBuildTask>
<HybridizerBinaryPath>{HybridizerPath}\Hybridizer.exe</HybridizerBinaryPath>
<Platform>x64</Platform>
</PropertyGroup>
<UsingTask AssemblyFile="$(HybridizerBuildTask)"
TaskName="Hybridizer.VSIntegration.BuildSatelliteTask.BuildSatelliteTask" />
<Target Name="Build">
<MakeDir Directories="generated-sources"/>
<BuildSatelliteTask
DllFullPath="MyProject.dll"
ResultFileName="MyProject.CUDA.xml"
GenerateLineInformation="true"
WorkingDirectory="generated-sources"
Flavors="CUDA" />
</Target>
</Project>
Step 3: Configuration File
The configuration file holds all functions to be transformed, including:
- EntryPoints: Methods called from host
- Kernels: Device-side methods
Configuration File Structure
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<HybridizerMetaConfigFile>
<ConfigFile
DllFullPath="MyApp.exe"
PdbFullPath="MyApp.pdb"
GenerateLineInformation="true"
UseFunctionPointers="true">
<HybridFlavor
FlavorName="CUDA"
GenerateCWrapper="true"
BuiltInFileNames="hybridizer.c.builtins;" />
<HybridElements HybridType="MyClass">
<HybridizedMethod MethodName="Algorithm">
<ParameterTypes>
<string>System.Double</string>
</ParameterTypes>
</HybridizedMethod>
</HybridElements>
</ConfigFile>
</HybridizerMetaConfigFile>
Key Configuration Options
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
GenerateLineInformation | Include debug line mappings |
UseFunctionPointers | Enable function pointer support |
GenerateHiddenStubs | Generate stubs for internal methods |
DelegateSupport | Enable delegate transformation |
UseHybridArrays | Use Hybridizer array types |
Step 4: Flavor Code Generation
Based on the configuration file, the Hybridizer generates source code for the selected flavor:
| Flavor | Output Files | Compiler |
|---|---|---|
| CUDA | .cu, .cuh | nvcc |
| OMP | .cpp, .h | g++ -fopenmp |
| AVX | .cpp, .h | g++ -mavx |
Each source file includes a sub-configuration comment for reproducibility.
Hybridizer Community Edition Integration
Hybridizer Community Edition wraps all these steps in its Visual Studio integration, providing a seamless build experience.
Supported Inputs
MSIL (.NET)
The Hybridizer operates on Microsoft Intermediate Language in binary form (.NET assembly). With associated attributes, the assembly is processed, extracting methods that need to be transformed.
Next Steps
- Invoke Generated Code — Call kernels from host
- Generated Code Layout — Understand output structure
- Line Info & Debug — Debugging support