CUDA Backend
For the CUDA flavor, the Hybridizer generates source code (or binaries) as .cu files that can be compiled by the NVIDIA CUDA C compiler (nvcc). Methods are declared using __device__ or __global__ attributes depending on whether they are called from the host or the device.
CUDA Overview
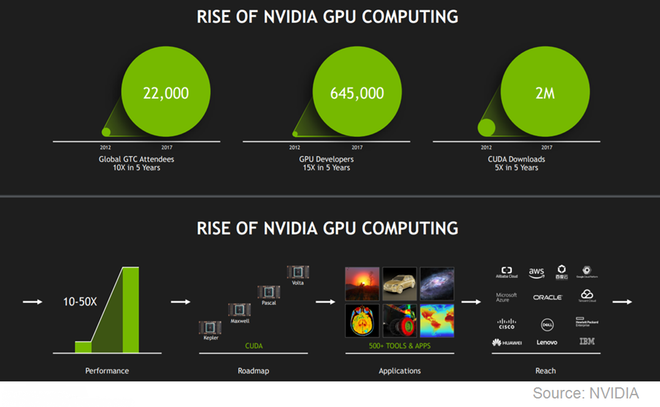
CUDA has wide adoption in the massively parallel computing community:
- Half a billion CUDA-capable GPUs worldwide
- 1.6 million CUDA downloads
- Used in many high-end supercomputers
Work Distribution in CUDA
Work distribution on CUDA is done with blocks and threads:
- Threads: Units of work execution
- Blocks: Groups of threads that can share memory
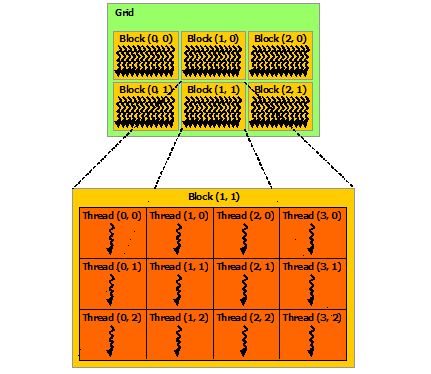
Threads in the same block can share data via shared memory, while blocks are more independent.
Naming Conventions and Intrinsics
In Hybridizer, work distribution uses the same CUDA terminology. For the CUDA flavor, there is a one-to-one mapping:
| Hybridizer | CUDA |
|---|---|
threadIdx.x | threadIdx.x |
blockIdx.x | blockIdx.x |
blockDim.x | blockDim.x |
gridDim.x | gridDim.x |
Intrinsics
Any method or property getter may be marked with an Intrinsic attribute:
// IntrinsicConstant maps to a CUDA constant
[IntrinsicConstant("threadIdx.x")]
public static int ThreadIdxX { get; }
// IntrinsicFunction maps to a CUDA function
[IntrinsicFunction("__syncthreads")]
public static void SyncThreads() { }
Example: Vector Square
[EntryPoint]
public void Square(int count, double[] a, double[] b)
{
for (int k = threadIdx.x + blockDim.x * blockIdx.x;
k < count;
k += blockDim.x * gridDim.x)
{
b[k] = a[k] * a[k];
}
}
CUDA-Specific Features
CUDA offers features not present in other hardware architectures:
| Feature | Description | Cross-Platform? |
|---|---|---|
| Shared Memory | Fast on-chip memory shared within a block | Mapped to stack memory |
| Shuffle Instructions | Data exchange within a warp | GPU-specific |
| Atomic Operations | Thread-safe memory operations | Partially supported |
| Dynamic Parallelism | Kernels launching kernels | GPU-specific |
Shared memory can be mapped to stack memory on CPU targets, mimicking the cache behavior.
Requirements
- NVIDIA GPU with CUDA Compute Capability 3.0+
- CUDA Toolkit installed
- Compatible driver
Performance Considerations
- Consider data transfer costs between host and device
- Use streams for overlapping computation and data transfer
- Profile with NVIDIA Nsight or nvprof
- See Memory & Profiling for details
Next Steps
- CUDA Basics: Threading — Deep dive into thread hierarchy
- CUDA Functions — Kernel and device functions
- Memory & Profiling — Optimization techniques